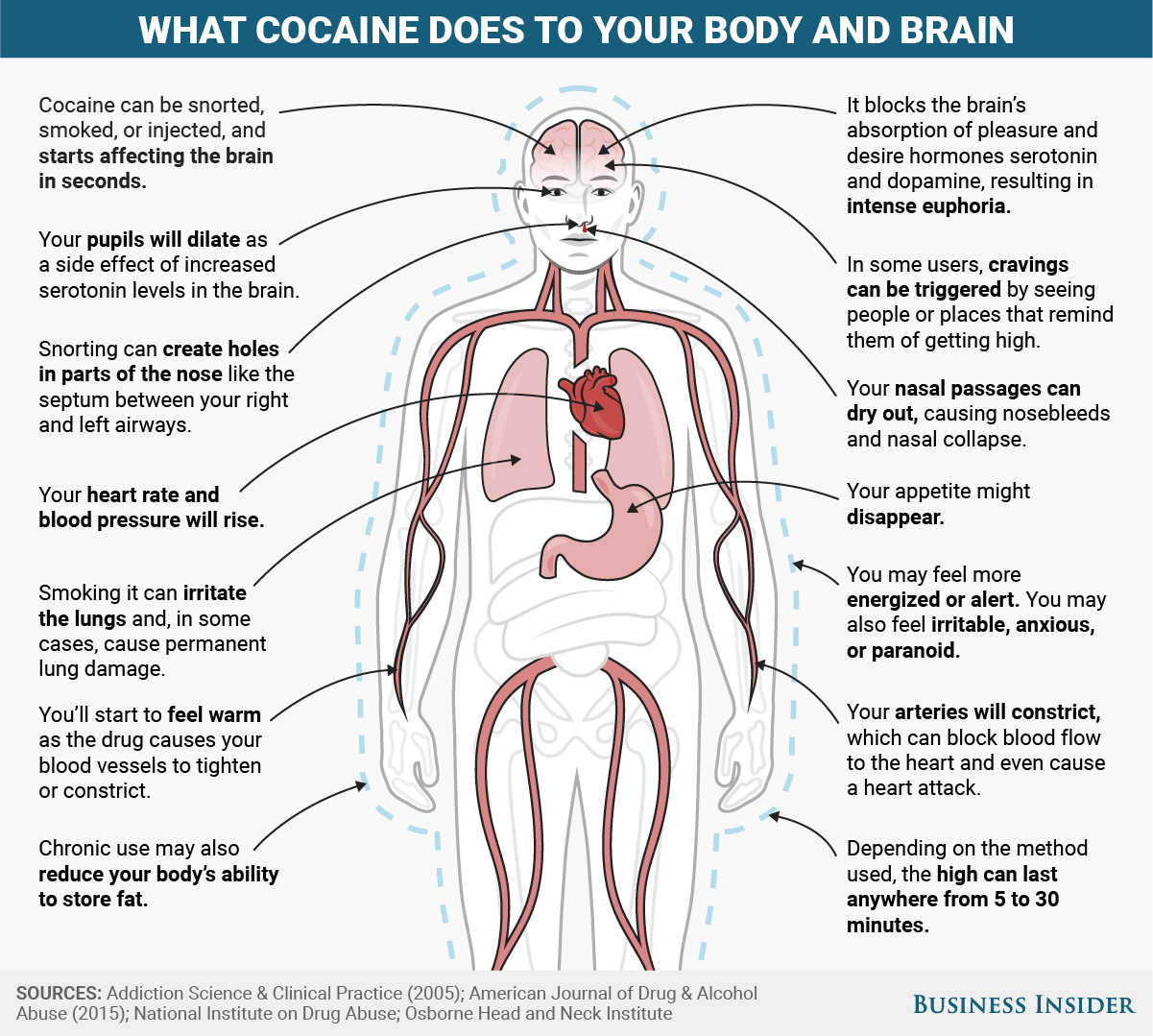
Cocaine interferes with the way our brain absorbs and recycles certain hormones, including those that play key roles in pleasure, desire, and drive. It also appears to acutely affect parts of our brain that play a role in forming and retrieving memories, which may influence our chances of becoming addicted.